Lecture 01: UNIX and You
Table of Contents
1 What is this class about?
IC221 is about Systems Programming and the UNIX environment
- User interacting with the OS through the shell and command line tools
- Programs interaction with the OS through the System Call API
- Programs interacting with Other Programs through the Operating System
- Programs interaction with Other Programs on Different Systems
1.1 Goals:
- You will learn the standard UNIX command line tools
- You will learn simple shell interaction and scripting
- You will learn to program in C and use the OS System Call API
- You will learn the process life cycle
- You will learn inter-process communication
- You will learn how to interact with the file system
- You will learn how to communicate over the network
- You will learn about process concurrency
1.2 Why is this class important?
- In IC210 you learned how to think algorithmically without much concern for the system that executes your code
- In IC221 you pull back the covers and see how the OS supports your program. For example, to print, the terminal requires a huge effort from the OS, which you will learn in detail.
- In IC221 you learn to interact with the OS on multiple levels: user-to-shell, program-to-OS, and system-to-system
- In IC221 you will become competent users of UNIX and the C programming interface, which is vital to understanding systems computing.
2 The 1000 Foot View of the UNIX system
Why UNIX?
- UNIX is an important OS in the history of computing
- Two major OS'es variants, UNIX-based and Windows-Based
- Used in a lot of back-end systems and personal computing
- UNIX derivatives are open source and well known to the community and developed in the open where we can study and understand them.
- The skills you learn on UNIX will easily translate to other OS platforms because all UNIX-based systems share standard characteristics.
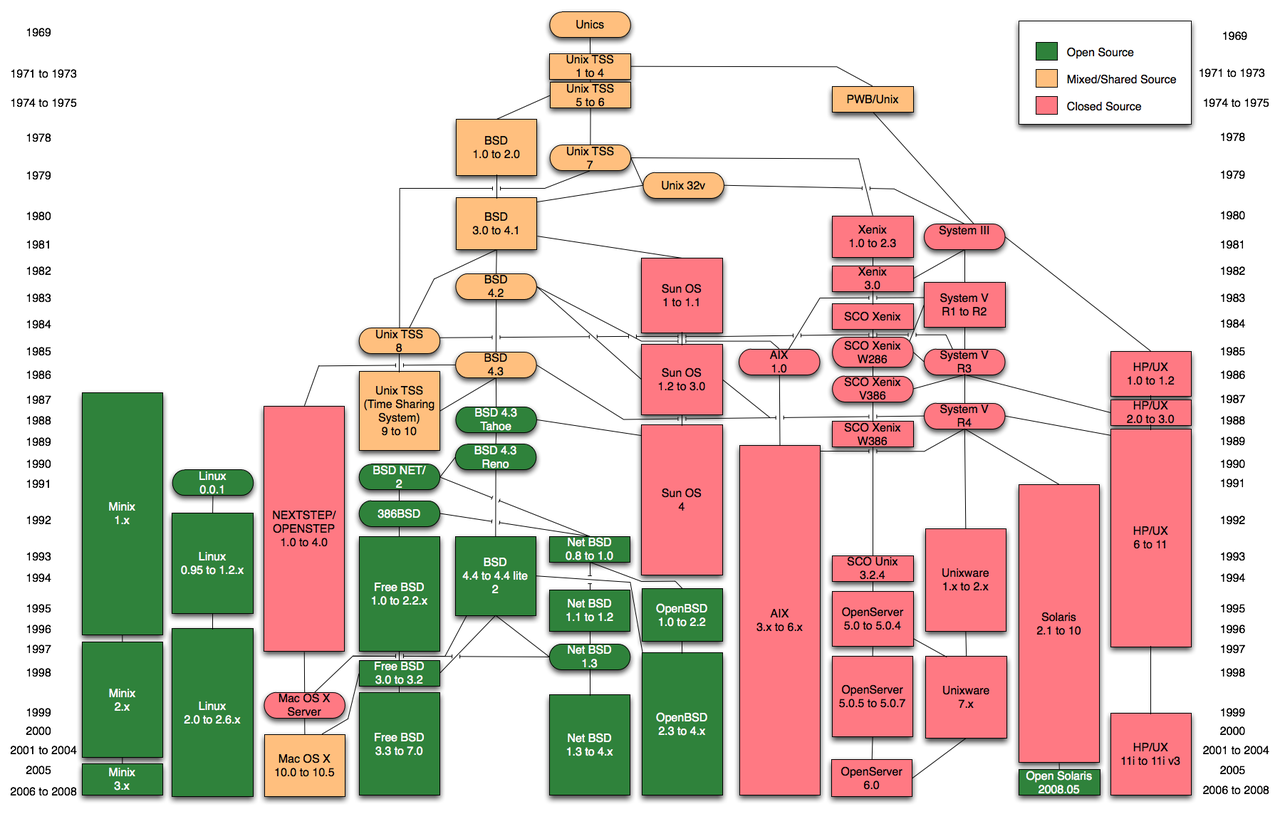
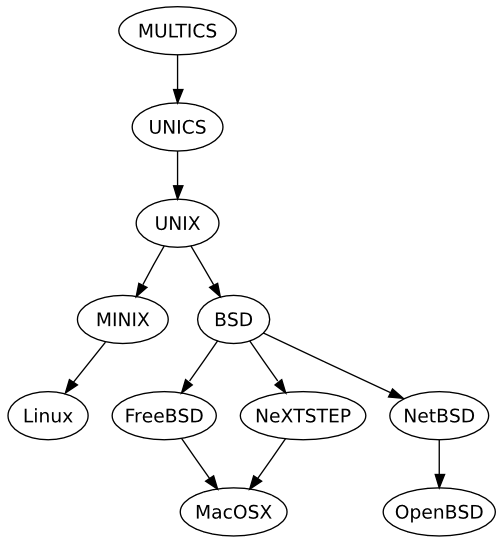
2.1 Unix History
Unix has a rich history dating back to the development of Multics and then Unic system. First developed at AT&T Bell labs in the early 70's. These early forms have dispersed and integrated into computing, include the Ubuntu, Debian Linux Variants variants we use here and the MacOS, BSD variants. Unix is even run on the mobile platforms, both iOS and Android are based on Unix system architecture.
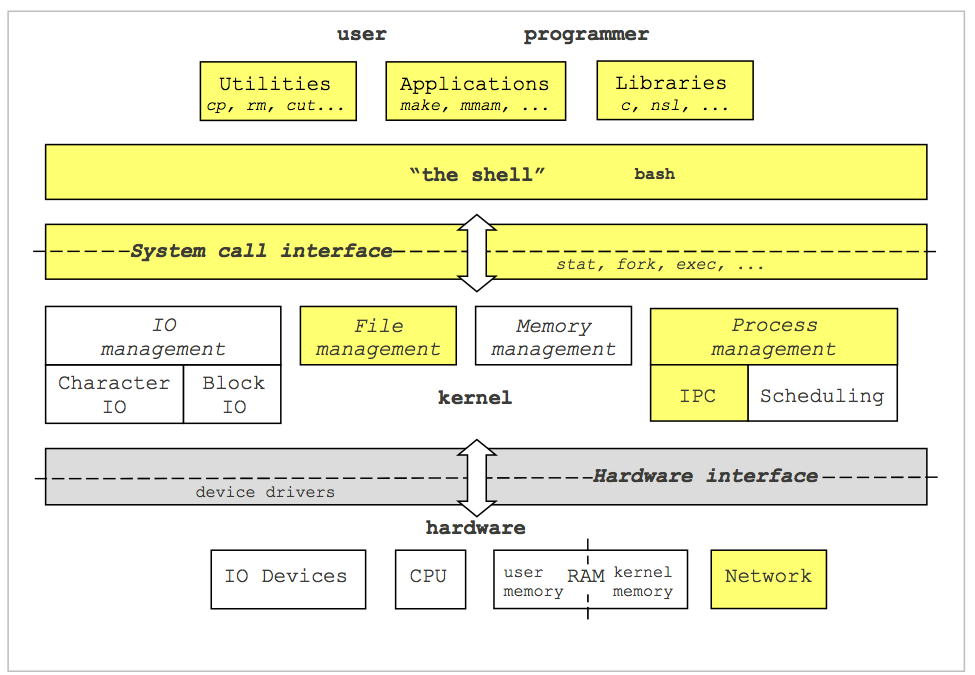
2.2 The Unix Components
The Unix-Computer ecosystem can be divided into three main parts:
- User Space: Defines the applications, libraries, and standard utilities that are user accessible. When we write a program, it is from this perspective that we operate, without concern for the underlying components. For example, writing a "Hello World" program on any computer is the same from the user-perspective, but might be different when it comes to actually executing the program and writing "Hello World" to the terminal.
- Kernel Space: This refers to the operations of OS that manage the interface between user actions and the hardware. It is the central part of the OS, and its primary job is to pair user applications with the underlying hardware and allow multiple programs to share singular hardware components. For example, how does a user input event, such as typing 'a' on the keyboard, get translated into 'a' appearing on the screen? Or, how does two programs both read from disc at the same time or run on the CPU at the same time?
- Hardware: The underlying physical components of the computer. These include Input/Output devices, like keyboards and monitors, the CPU which does calculations, the memory components, and the network interface.
The OS'es primary task is to manage services as an interface between the user and the hardware. Examples include:
- File System: managing files on the user
- Device I/O: managing input from devices
- Processes: Starting, running, and stopping programs, and allowing multiple programs to run at once, i.e., program multiplexing
- Memory Management: Allocating runtime memory for process and separating memory between process and between user-space and the kernel-space
From a user of the OS, you will see these interactions from two perspectives:
- Shell: You will use the shell to interact with the OS
- System Call API: You will program in C to interact with the OS
Why C?
- C is a low level language
- The OS is written in C
- Understanding the OS and C together is a natural process and will make you a better programmer
3 Where we will go in this course
This course consists of 4 major units:
- Shell: Becoming proficient at interacting with the OS through the shell
- C Programming: Becoming proficient at interacting with OS with C
- OS Interfaces: Interacting with the I/O devices through the file manipulation and the network, and understand the security services.
- Concurrency: Managing processes/threads competing for a single resource